Bacterial Colonisation
on Blood Pressure Cuffs





Single Patient Use Solution

Key Benefits


REDUCED RISKS

IMPROVE FINANCIAL OUTCOMES

ENHANCED PATIENT SAFETY

DISPOSABLE SINGLE PATIENT USE
For a FREE Review of the blood pressure cuffs in your department.
Disposable Cuffs are recommended in Guidelines for prevention and control of infection
With around 200,000 healthcare-associated infections in Australian acute healthcare facilities each year³, the problem does not just affect patients and workers in hospitals. It can occur in any healthcare setting including office-based practices. Any person working in or entering a health care facility is at risk.
Recommendation: “Use patient-dedicated equipment or single-use non-critical patient-care equipment . . .”4


“There is clear evidence that certain infectious agents are transmitted by direct or indirect contact during patient care . . . Indirect transmission involves transfer of an infectious agent through a contaminated intermediate object or person . ." 4
Clinical Evidence


CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTION
Clostridium difficile infection is one of the most common HAI in Australia,with an annual incidence of 3.65 per 10,000 bed days and an attributable mortality rate of 6–7% at 30 days.
Reference: Leffler DA, Lamont JT. Clostridium difficile infection. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1539–48.

THE COST OF HAI’s TO AUSTRALIA
It’s estimated that 200K HAIs occur annually in Australia, of which 50% are preventable.
Two million hospital bed days are lost to HAI annually, with an estimated value of more than $1 billion.
Reference: Fernando, S et. al. (2017) Healthcare-acquired infections: prevention strategies. Internal Medicine Journal, 47: 1341-1351.

HAIs: A GROWING PROBLEM WORLDWIDE
Hospital Acquired Infection or Healthcare Associated Infection (HAI) is a growing problem worldwide. On a given day, about 1 in 31 hospital patients has at least one healthcare-associated infection.
Reference: CDC HAI Report October 5, 2018

SINGLE PATIENT USE BP CUFFS BREAK THE CHAIN OF INFECTION
A workflow where each patient gets a new disposable blood pressure cuff is a simple way to reduce risk associated with HAIs. One study showed bacteria was still present after reprocessing and reusing blood pressure cuffs.*.
Implementation of Disposable Blood Pressure Cuffs as a Novel Approach to Reduce Fomite Transmission of Healthcare-Associated (HCA) Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) in a Community Hospital or Twice Implemented is Once Credible. American Journal of Infection Control, Volume 37 Issue 5 , E61 - E62.

CLEANING AND DISINFECTION OF BLOOD PRESSURE CUFFS
Disinfecting and cleaning is by far the most common method used which is economical and cost effective but even after cleaning organisms are still cultured from BP cuffs which is similar to our study where Klebsiella pneumonia was isolated even after cleaning with 70% isopropyl alcohol.
Reference: Jeyakumari D et. al. (2016) Bacterial colonization of blood pressure cuff: A potential source of pathogenic organism: A prospective study in a teaching hospital. International Journal of Medical and Health Research, 2 (6): 35-37.
“The high rate of BP cuff contamination (82.1%) observed in this study was not a surprise, as no other piece of hospital equipment was in more common use without adequate disinfection…”
Reference: C.J. Uneke et. Al. (2011) The Potential for Transmission of Hospital-Acquired Infections by Non-critical Medical Devices: The Role of Thermometers and Blood Pressure Cuffs, World Health & Population 12 (3) :5-12.
A recent study investigating a specific outbreak in St. Augustine’s Hospital found that most spread appeared to be facilitated by staff and patient movement as well as through shared equipment including thermometers, stethoscopes and blood pressure cuffs.
Reference: Report into a nosocomial outbreak at Netcare St. Augustine’s Hospital Lessells R, Moosa Y, de Oliveira T. 15 May 2020. Available at: https://www.krisp.org.za/manuscripts/StAugustinesHospitalOutbreakInvestigation_FinalReport_15may2020_comp.pdf.
A recent study showed that mild upper respiratory tract involvement in a SAR-CoV-2 infected patient resulted in extensive environmental surface contamination, including the stethoscope.
Reference: Air, surface environmental, and personal protective equipment contamination by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV-2) from a symptomatic patient Ong SWX, Tan YK, Chia PY, Lee TH, Ng OT, Wong MSY, Marimuthu K. JAMA. 2020;323:1610–1612.
In a study examining contamination rates of keyboards in teaching hospitals, 100 keyboards in 29 clinical areas were tested for bacterial contamination. Of those, 95% tested positive for microorganisms.
Reference: Maureen Schultz, MSN, CIC; Janet Gill, BSN, CIC; Sabiha Zubairi, MT; Ruth Huber, MS, CIC; Fred Gordin, MD; Bacterial Contamination of Computer Keyboards in a Teaching Hospital, The University of Chicago Press and The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, INFECTION CONTROL AND HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY CONCISE COMMUNICATIONS April 2003, Vol. 24 No. 4.
Setting up an Isolation Room
Exploring the clinical evidence above, it implicates the use of medical devices such as sphygmomanometers, thermometers, stethoscopes, and reusable blood pressure cuffs in the spread of HAI's.
Baxter can help.
Disposable and dedicated medical devices and equipment can reduce the risk of cross-contamination and are a proven method of successfully reducing HAIs. Baxter offers a range of products providing your facility with an easy, cost-effective solution, from disposable blood pressure cuffs to blood pressure devices and ECG’s – which can help reduce the risk of cross-contamination, one patient at a time.
Product Focus



Welch Allyn
FlexiPort EcoCuff Single Patient Use Blood Pressure Cuffs
QUICK OVERVIEW:
Lower your risk of cross-contamination. Control costs. Reduce your hospital's environmental impact. With FlexiPort EcoCuff Single Patient use Blood Pressure Cuffs, it's not just possible - it's simple.
FEATURES:
- FlexiPort technology enables every cuff to be used as one or two-tube.
- Durable enough to last for a complete patient stay
- Features the Welch Allyn FlexiPort single-point connection port
- Slot-fitting system helps prevent mis-cuffing
- Recyclable
- Up to 60% lower environmental impact than traditional blood pressure cuffs
- Meets all the latest clinical guidelines for proper fit from AAMI and AHA
- Does not contain BPA, DEHP, Latex or PVC

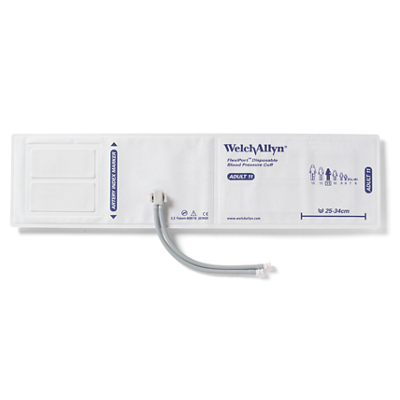

Welch Allyn
FlexiPort Disposable Blood Pressure Cuffs
QUICK OVERVIEW:
When it comes to standardising blood pressure cuffs, Welch Allyn FlexiPort blood pressure cuffs can help facilities improve financial outcomes and enhance patient safety with options that help streamline workflow and inventory management and reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
FEATURES:
- FlexiPort technology enables every cuff to be used as one or two-tube.
- Durable enough for extended patient stays.
- Affordable for single-patient use to help reduce cross-contamination risk.
- Port can be rotated for improved patient comfort
- Pair the FlexiPort Blood Pressure Cuffs with one of our Welch Allyn multiparameter vital signs monitors.

Welch Allyn
Spot Vital Signs 4400 Device
QUICK OVERVIEW:
The Spot Vital Signs 4400 Device delivers a digital, consolidated way to capture your patient’s vitals with a simple touchscreen display. Quickly capture a full set of patient vital signs—including temperature, blood pressure, pulse rate and SpO2 – right from the home screen in about 60 seconds.
FEATURES:
- Options for documenting patient observations (i.e. Respiration Rate, BMI). Durable enough for extended patient stays.
- Can be used one-per-room to align with WHO’s recommendation of dedicated monitor-to-patient for isolation, infection prevention and control.

Welch Allyn
Connex Spot Monitor
QUICK OVERVIEW:
Easy-to-use and provides accurate vital signs measurement including blood pressure averaging, digital respiration rate, spot checking, interval monitoring and custom scoring across patient populations.
FEATURES:
- Limits clinician exposure to infected patients.
- Aligns to WHO’s recommendation of dedicated monitor-to-patient for isolation, infection prevention and control.
- Automated Early Warning Scoring to help clinicians identify and respond to signs of patient deterioration (i.e. MEWS, NEWS).
KEY TAKEAWAYS

REFERENCE: WHO: The Burden of Health Care-Associated Infection Worldwide, A Summary, 2010.

REFERENCE: Chowdhary, A et. al. (2016) Multidrug-resistant Candida auris: 'new kid on the block' in hospital-assoclated infections? 94: 209-212.

REFERENCE: Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council. (2010) Australlan Guideline for the Prevention and Control of Infection in Healthcare, accessed from https: www.nhmrc.gov.au on 22 August 2018.
Contact Us
To learn more or to speak directly with a Baxter representative concerning our products, services, operations or locations, please complete the form below or contact our Customer Care on 1800 445 576.

